
This 3-element Yagi Antenna calculator is useful to design the Yagi Antenna. Reflector to Dipole Spacing = 0.1875 meters,ĭipole to Director Spacing = 0.1875 metersįormula/Equations used in Yagi Antenna Calculatorįollowing formula/equations are used in the Yagi Antenna Calculator.
OUTPUTS: Reflector Length = 0.7425 meters, Dipole Length = 0.7095 meters,
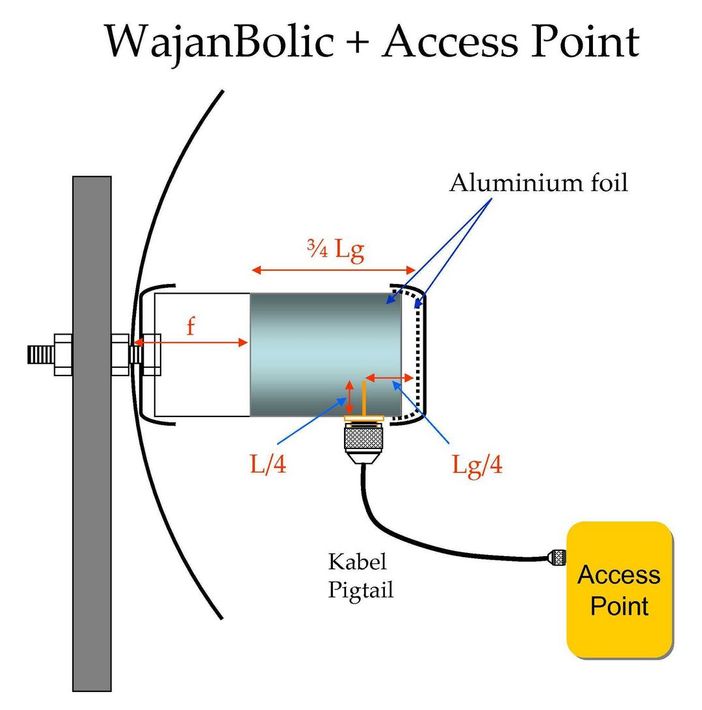
5GHZ CANTENNA CALCULATOR PATCH
The calculators for other antenna types such as parabolic,horn,dipole and patch are also mentioned. The formula and basics of Yagi Antenna Calculator are also explained with example. This page covers 3 element Yagi Antenna calculator. Maximum range is achieved through the use of powerful receivers and transmitters as well as a clear line of sight between them.3 element Yagi Antenna Calculator | Yagi Antenna Calculator NOTE: All range data is under ideal circumstance but will perform in the ball park. Keeping that in mind and thinking about what your specific needs are you can begin to narrow down what antenna is best for you. The higher the dBi rating the larger the area the signal covers. Each specific antenna has a gain rating or dBi (decibel isotropic) number which coincides with the performance. Omni WiFi antennas do not need to be pointed since their radiation cone is 360 degrees, working in all directions. Omni directional antennas are most commonly are used to create hot spots by transmitting a signal over a large area in all directions or receiving signals in all directions when the transmit location is unknown or close by.

As a rule of thumb to remember, high dBi rating = further distance covered but not area. The higher the dBi rating the narrower the reception cone and knowing these data points you can then begin to narrow down the right antenna for you. A good way to start without seeing actual lab data or knowing the specs is to judge by the dBi (decibel isotropic) rating. The way to ensure your aim is best is to know the width of the reception cone in which the antenna has. When it comes to aiming the antenna the user must be right on the signal for the best strength and quality.

Unlike omnidirectional antennas, directionals must be aimed in the direction of the signal transmitter or receiver which can be for example a router or WiFi hotspot. Directional antennas as the name implies refers to signal coverage in a specified direction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
